A Change in the Order of Dna Bases That Code
However scientists were not sure how they would be arranged in a DNA molecule. There are chemical bonds between the two strands in DNA formed by pairs of bases.

Dna Structure 6 1 5 Aqa Gcse Biology Revision Notes 2018 Save My Exams
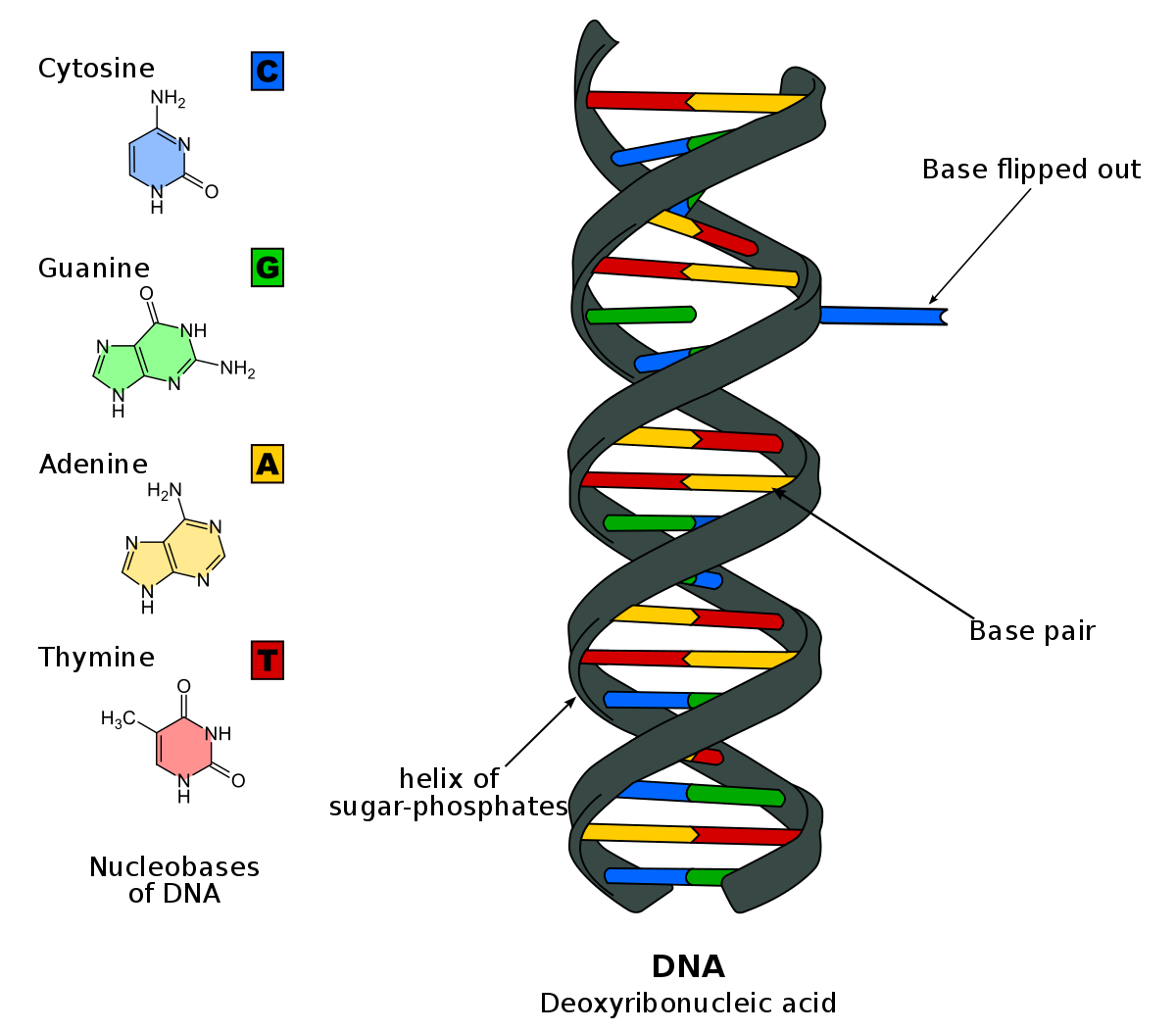
The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder.

. The cell reads the sequence of the gene in groups of three bases. A gene mutation is an alteration in the sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Copying errors when DNA replicates or is transcribed into RNA can cause changes in the sequence of bases which makes up the genetic code.
Mutations change the order in which the organic bases are in your DNA. The synonymous codons for the amino acids and their depiction in IUB codes Nomenclature Committee 1985 Eur. Amino acids are then joined in this order to make the protein.
A change in the order of DNA bases that code for a respiratory protein will most likely cause A The production of a starch that has a similar functionB The digestion of the altar gene by enzymesC A change in the sequence of amino acids determined by the geneD The release of antibodies by certain cells to correct the error. It was the evidence provided by Rosalind Franklin in 1952 that helped James D Watson and Francis Crick to build their model of a DNA molecule. 1501-5 are also shown.
1st base 2nd base 3rd base U C A G U. UCA UAA Stop Ochre UGA Stop Opal A UUG. Altering nucleotide sequences most often results in non-functioning proteins.
There are four different bases in DNA. Changes to individual bases. These bases code for proteins and if they change so the code changes.
A change in the sequence of amino acids determined by. Remember that a set of three bases in a gene in DNA codes. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases with adenine forming a base.
Radiation and some chemicals can also cause changes. The standard ambiguity codes for nucleotides and for the one-letter and three-letter designations of amino acids are given. In order to understand these secret messages we would need to know the code and apply the same set of rules in reverse to decode it.
The release of antibodies by certain cells to correct the error. Mating two living things. This change can affect a single nucleotide pair or larger segments of a chromosomes.
UCG UAG Stop Amber UGG TrpW Tryptophan. There are four different bases in DNA. If the U is mutated to C the mRNA will still encode for the amino acid proline.
A change in the order of DNA bases that code for a respiratory protein will most likely cause a. DNA changes occur primarily because of natural errors that occur during the DNA replication process. Three bases a base triplet code for one amino acid.
These bases are found in the centre of a DNA molecule. 69 rows Standard genetic code. This is because changes in the nucleotide sequences change the codons.
Incorrect Answers If the U is mutated to C. In this article well take a closer look at the genetic code which allows DNA and RNA sequences to be decoded into the amino acids of proteins. The DNA messages depends on the order of the.
The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of DNA bases A C G and T in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes. The digestion of the altered gene by enzymes c. Besides the nitrogen bases DNA contains sugar and.
A change in the order of DNA bases that code for respiratory protein will most likely cause. They also can happen when one or more environmental factors act on the DNA. A change in the sequence of amino acids determined by the gene d.
Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar deoxyribose and phosphate groups. Due to redundancy in the genetic code a change in the third nucleotide of a codon often leads to no change in the amino acid sequence. The examples which follow show some of the easier-to-understand effects of this.
A change in the code can mean a different protein is. There are 64 different. A codon is a trinucleotide sequence of DNA or RNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid.
The DNA code sequence of bases is found on the coding strand. Standard Ambiguity Codes. DNA forms the code for the making of.
Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine A cytosine C guanine G or thymine T. The production of a starch that has a similar function b. A change in DNA code.
There are chemical cross-links between the two strands in DNA. CUU CCU ProP Proline. An exact copy of.
U UUC UCC UAC UGC C UUA LeuL Leucine.

Nucleic Acids To Amino Acids Dna Specifies Protein Learn Science At Scitable

Comments
Post a Comment