Describe the Role of Insulin in Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
Insulin then helps move the sugar from the blood into your cells. As the glucose level falls the insulin level also falls so that the individual doesnt get hypoglycemia.

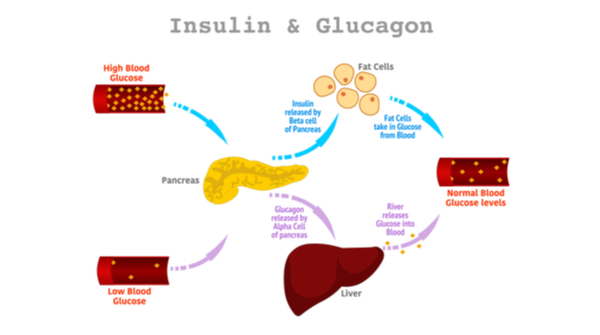
2 Regulation Of Blood Glucose Levels By Insulin And Glucagon When Download Scientific Diagram
Glucagon raises blood sugar levels whereas insulin lowers blood sugar levels.

. Insulin is a hormone which plays a key role in the regulation of blood glucose levels. Insulin and glucagon work together to balance your blood sugar levels keeping them in the narrow range that your body requires. These hormones are like the yin and yang of blood glucose maintenance.
After a meal the islets release insulin which ushers glucose from the blood stream into the bodys cells for immediate use in the production of energy or into the liver and fat cells for storage. After you eat carbohydrates break down into glucose a sugar that is the bodys primary source of energy. - increase in blood sugar.
Insulin and glucagon are hormones that help to regulate blood sugar levels. How To Regulate Blood Sugar At Night But looking describe the role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels at is diabetic medicine expensive the long distance relationships around me my confidence began to shake if I meet someone I like but diabetes prevention program diet can t stay in a city will I still start this relationship. When blood glucose levels rise insulin is secreted by the pancreas lowering blood glucose by increasing its uptake in cells and stimulating the liver to convert glucose to glycogen in which form it can be stored.
- glucose leaves blood. This increases expression of mTOR which will cause increased transcription of glucose transpo View the full answer. The role of insulin in the body.
This secretion happens as per the glucose level in the blood. - binds to specific receptors on liver muscle cells. In addition to its role in controlling blood sugar levels insulin is also involved in the storage of fat.
Insulin binds to its receptor in the cell membrane and induced PI3 kinase signaling. In this way insulin and glucagon work together to maintain homeostatic glucose levels as shown in Figure 1911. The pancreas responds by producing insulin which allows glucose to enter the bodys cells to provide energy.
The blood glucose range is 140 mgdl and decreases due. Insulin is the hormone that causes entry of glucose into the cell. When you eat your body breaks food down into sugar and sends it into the blood.
In a sense the role of insulin is to maintain the glucose level of the body and keep one away from disease. When sugar enters your cells it is either used as fuel for energy right away or stored for later use. Rising blood glucose levels inhibit further glucagon release by the pancreas via a negative feedback mechanism.
The pancreatic cells that produce glucagon are called alpha cells. The two hormones work together and if even one does not function right then it can cause an imbalance in blood sugar levels. Insulin is produced by specialized beta cells in the pancreas which are clustered into groups called islets of Langerhans or islets for short.
When people develop diabetes they can regulate their blood sugar levels by injecting insulin. In simple words when sugar is high the pancreas secretes more insulin and when blood sugar levels drop they release glucagon to bring it back. If you dont have diabetes insulin helps.
There is a direct relationship between glucose and insulin. That has been the story ever sincediabetes is a. Insulins overall role is to control energy conservation and utilization during feeding and fasting states.
7 we observe the decrease of blood glucose level when insulin is given as an external source. A lack of insulin or an inability to adequately respond to insulin can each lead to the development of the symptoms of diabetes. Art Connection Figure 1911 Insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose levels.
Regulate blood sugar levels. Simulation of SoM with insulin infusion. The endocrine function of the pancreas is to produce insulin and another hormone called glucagon that helps regulate blood sugar.
By monitoring glucose levels amino acids keto acids and fatty acids circulating within the plasma beta cells regulate the production of insulin accordingly. Insulin and glucagon work together to balance your blood sugar levels keeping them in the narrow range that your body requires. Insulin which lowers blood sugar and glucagon which raises it are the most well known of the hormones involved but more recent discoveries of other glucoregulatory.
Insulin and glucagon are hormones that help regulate the levels of blood glucose or sugar in your body. Beta cells are responsible for insulin synthesis. Suggest why it is important that muscle cells do not convert.
For a T1DM external infusion of insulin is required for regulating the blood glucose level and maintaining it within the threshold range. Glucose which comes from the food you eat moves through your bloodstream to help fuel your body. In imbalance of either of these important chemical messengers can play a huge role in diabetes.
- more glucose enters cells. Describe the role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels. This is also called hyperglycemia.
Which means insulin or glucagon is produced and released to regulate the blood sugar level in the body. The pancreas secretes insulin and glucagon both of which play a vital role in regulating sugar levels in the blood. Describe the role of insulin in control of blood glucose concentration.
- glucose entering cells converted to glycogen. Blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar primarily glucose are maintained by the body within a narrow range. The distinction is in how each hormone contributes to blood sugar management.
Insulin is responsible for regulating the glucose concentration inside the bloodstream. Glucose then enters the bloodstream. This tight regulation is referred to as glucose homeostasis.

Role Of Insulin And Glucagon In Regulating Blood Glucose Levels Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment